
When it comes to analyzing operating expenses, managers classify the expenses as either fixed or variable. A fixed cost remains the same no matter what the production level is, while variable cost does vary with the number of products or services that a company produces. By https://www.iprofitpool.com/dev/what-is-the-double-declining-balance-method-of/ distinguishing between fixed and variable expenses, business owners can better predict and control their financial outflows. Regular review and analysis of operating expenses are essential for maintaining a competitive edge and maximizing profitability. Understanding how operating expenses affect these ratios can help you make informed decisions about cost management and operational efficiency.
- Operating expenses are the costs incurred by a business for its operational activities.
- This alignment greatly simplifies year-end tax preparation and ensures your regular financial reports directly support compliance requirements.
- While both are considered business expenses, operating expenses and COGS serve different purposes.
- Operating expenses are the costs that have been used up (expired) as part of a company’s main operating activities during the period shown in the heading of its income statement.
- By controlling and optimizing these expenses, businesses can enhance their margin, effectively converting a higher percentage of revenues into profits.
- For instance, a business with high operating expenses may be less attractive to investors and lenders as it could struggle to maintain adequate cash flows.
CapEx vs. OpEx
We handle the hard part of finding the right tax professional by matching you with a Pro who has the right experience to meet your unique needs and will handle filing operating expenses include which of the following? taxes for you. Save time with automated accounting—ideal for individuals and small businesses. Reconciling bank statements through this verification process compares recorded transactions against actual money movement through your accounts, revealing discrepancies before they become permanent problems. When your credit card statement shows an unfamiliar charge, reconciliation prompts investigation before incorrect data infiltrates your financial reports. Knowing the differences between wire transfers vs. ACH transfers and how they vary in speed, cost, and security is key for making informed decisions. By categorizing your expenses, you can better understand which areas are driving costs and where there may be room to optimize.
Transportation and Travel Costs

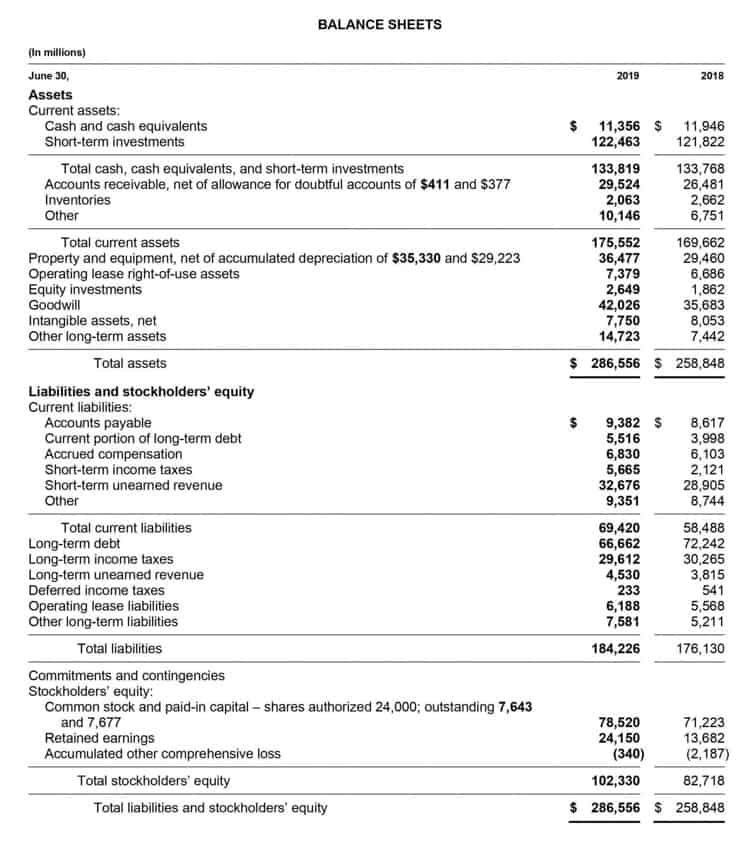
Operating expenses significantly influence a business’s performance by directly impacting profit margins and operating income. These expenses comprise the day-to-day costs required to keep a business running, such as salaries, rent, advertising, and maintenance costs. They play a critical role in determining a company’s financial health and profitability.
Examples of Compensation-Related Operating Expenses

Investors can use the Travel Agency Accounting data from Apple’s 10-K filings to examine total operating costs for several quarters or years. They can then compare these numbers to determine whether the company effectively manages operating costs over time. Unlike fixed costs, variable costs increase when production goes up and decrease when production drops. If a manufacturing company wants to increase production, it needs more raw materials.
- Knowing the differences between wire transfers vs. ACH transfers and how they vary in speed, cost, and security is key for making informed decisions.
- To find your company’s operating expenses, review your general ledger, and look for expenses that don’t directly impact the cost of creating your product or service.
- This process allows companies to track their spending and compare it with their actual performance.
- Other types not directly recorded in the income statement are Non-Cash Expenses, Prepaid Expenses, Accrued Expenses, Fixed Expenses, and Variable Expenses.
- When a retailer or manufacturer purchases inventory, these items are recorded on the balance sheet as assets rather than being immediately expensed.
- Let’s explore the process of determining your operating expenses and how to use this information effectively.
- It typically relates to recurring expenses such as rent, interest payments, insurance payments, and bank fees.
Operating expenses are prominently featured in a company’s income statement, reflecting the ongoing costs required to sustain its operations. On the other hand, non-operating expenses are disclosed separately to clarify their impact on the business’s overall financial performance. Operating expenses are a crucial aspect of any business’s financial management.

Consider aligning your internal expense categories with tax reporting requirements whenever possible. This alignment greatly simplifies year-end tax preparation and ensures your regular financial reports directly support compliance requirements. Many business owners discover that careful upfront category planning saves countless hours during tax season and financial reviews.
Operating Expense Ratios and Analysis
As the name suggests, operating expenses are expenditures needed for running a firm’s day-to-day operations. Some of a company’s operating costs may be considered semi-variable or semi-fixed. Operating costs are calculated by adding the cost of goods sold (COGS) and other operating expenses. Drastic cuts to operating costs can hurt profits over time by decreasing productivity and sales. If a company lays off three out of four customer service employees, payroll expenses will drop, leading to immediate savings while increasing short-term profits.


